- აფრიკული
- ალბანური
- ამჰარული
- არაბული
- სომხური
- აზერბაიჯანული
- ბასკური
- ბელორუსული
- ბენგალური
- ბოსნიური
- ბულგარული
- კატალანური
- სებუანო
- კორსიკული
- ხორვატული
- ჩეხური
- დანიური
- ჰოლანდიური
- ინგლისური
- ესპერანტო
- ესტონური
- ფინური
- ფრანგული
- ფრიზული
- გალისიური
- ქართული
- გერმანული
- ბერძნული
- გუჯარათული
- ჰაიტური კრეოლური
- ჰაუსა
- ჰავაის
- ებრაული
- არა
- მიაო
- უნგრული
- ისლანდიური
- იგბო
- ინდონეზიური
- ირლანდიური
- იტალიური
- იაპონური
- იავური
- კანადა
- ყაზახური
- ქმერული
- რუანდელი
- კორეული
- ქურთული
- ყირგიზული
- შრომა
- ლათინური
- ლატვიური
- ლიტვური
- ლუქსემბურგული
- მაკედონური
- მადაგასური
- მალაიური
- მალაიალამური
- მალტური
- მაორი
- მარათჰი
- მონღოლური
- მიანმარი
- ნეპალური
- ნორვეგიული
- ნორვეგიული
- ოქსიტანური
- პუშტუ
- სპარსული
- პოლონური
- პორტუგალიური
- პენჯაბური
- რუმინული
- Russian
- სამოური
- შოტლანდიური გელური
- სერბული
- ინგლისური
- შონა
- სინდური
- სინჰალური
- სლოვაკური
- სლოვენური
- სომალელი
- ესპანური
- სუნდური
- სუაჰილი
- შვედური
- ტაგალოგური
- ტაჯიკური
- ტამილური
- თათრული
- ტელუგუ
- ტაილანდური
- თურქული
- თურქმენული
- უკრაინული
- ურდუ
- უიღურული
- უზბეკური
- ვიეტნამური
- უელსური
- დახმარება
- იდიში
- იორუბა
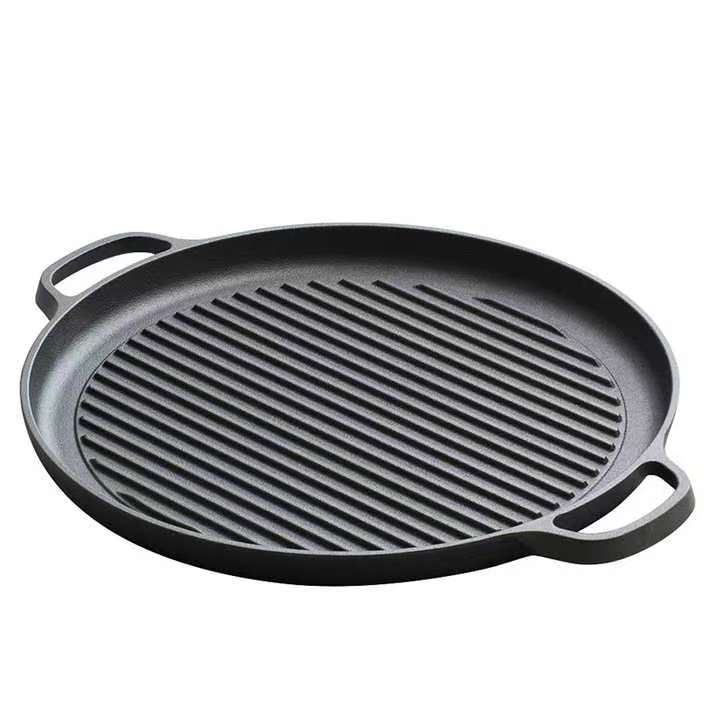
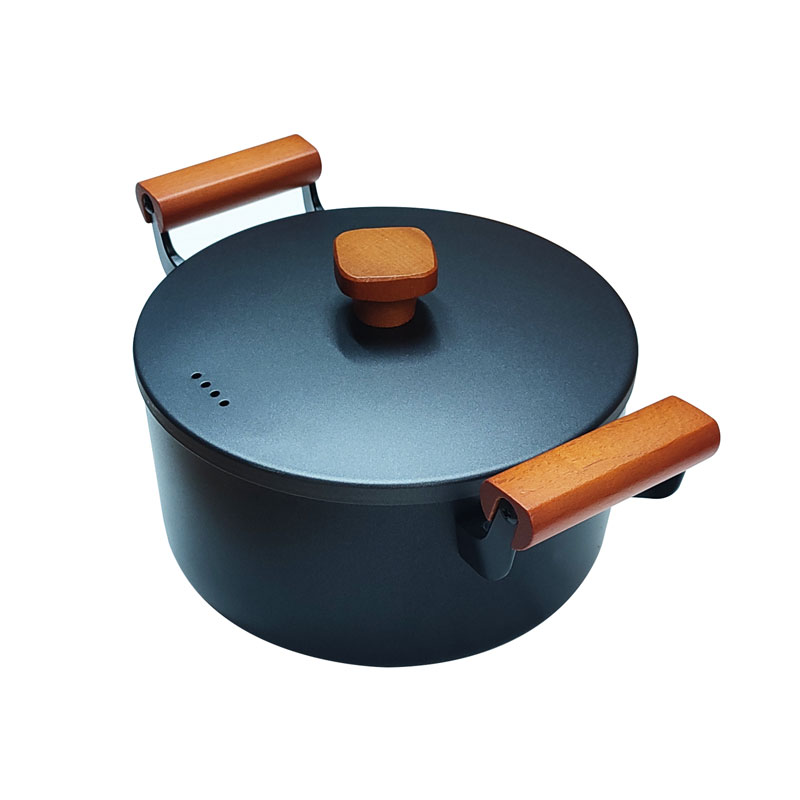
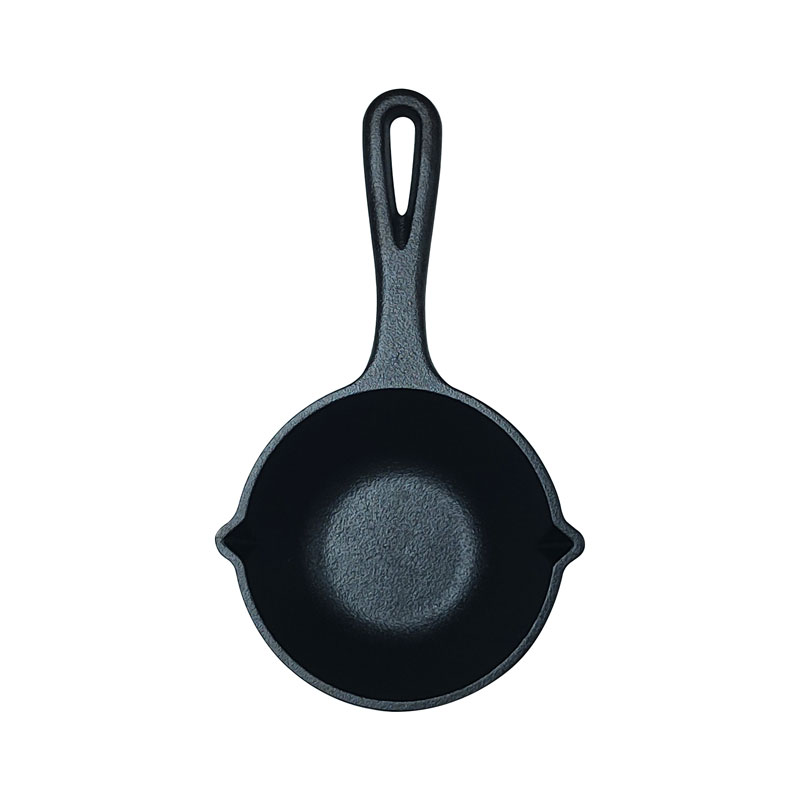
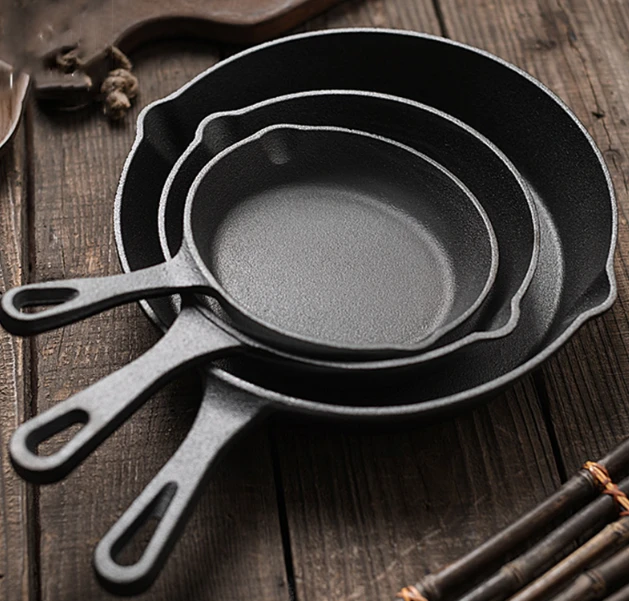
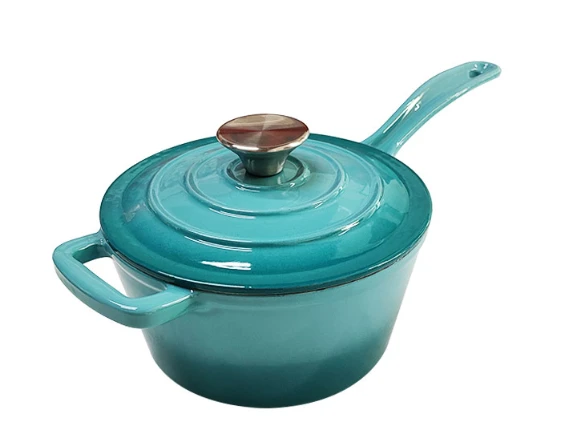
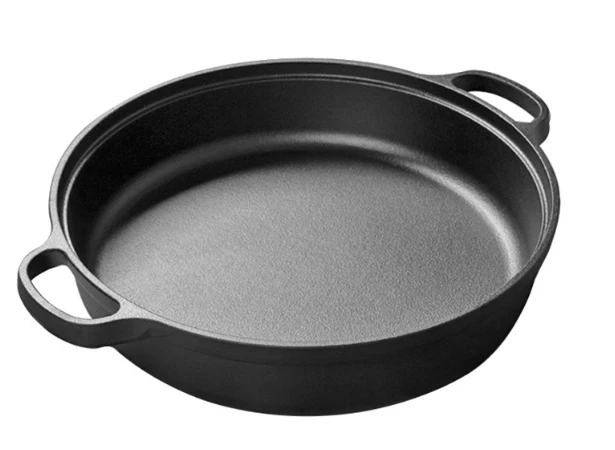
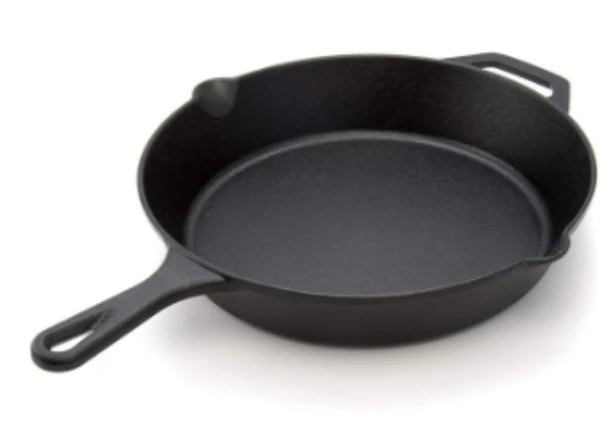
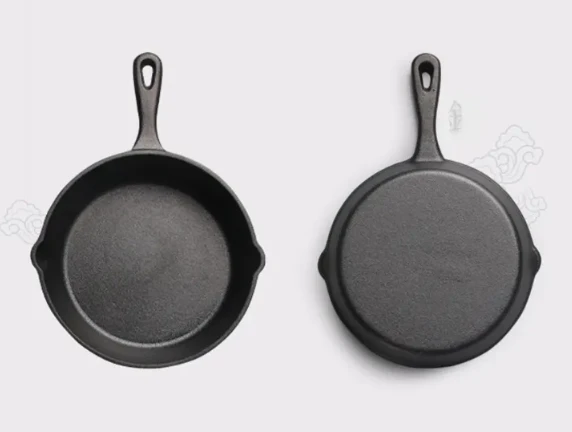
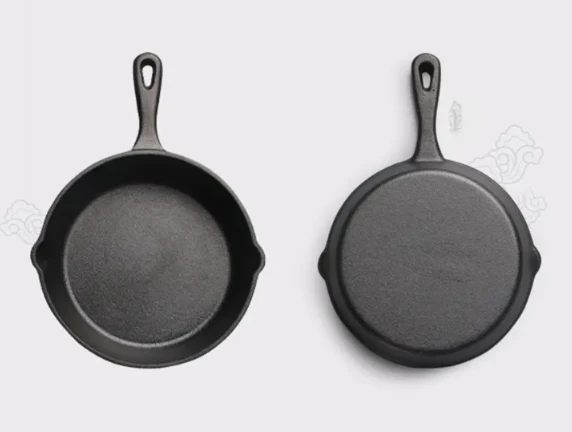
Pre-Seasoned Cast Iron Egg Frying Pan FAQ Guide
Is This Cast Iron Skillet Really Non-Stick?


Yes, it is pre-seasoned with natural oils, creating a non-stick surface that improves with continued use and proper care.
What Size Is This Skillet and How Many Eggs Can It Cook?


Sizes vary by model, but most are designed to cook 1 to 3 eggs at once—ideal for personal or small-batch cooking.
Can I Use This Skillet on All Heat Sources?


Yes, the skillet is compatible with induction, gas, electric, ceramic cooktops, and is also oven-safe (handle material permitting).
How Should I Clean the Pan Without Damaging the Seasoning?


Clean with warm water and a soft sponge. Avoid using soap or dishwasher. Dry immediately and apply a thin layer of oil after each use.
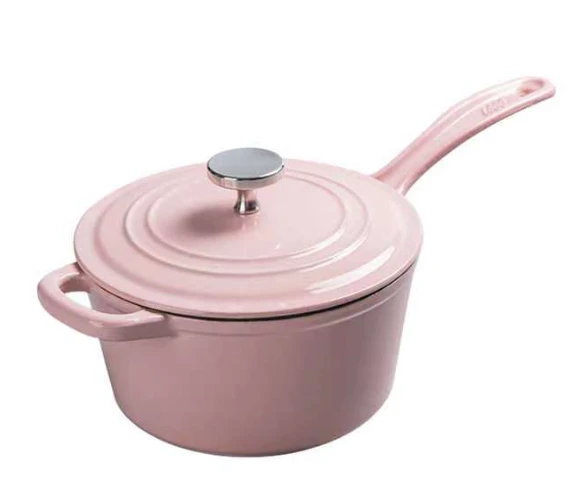
Is This Skillet Suitable for Wholesale or Custom Branding?


Yes, it’s available for bulk orders and supports custom logo branding, packaging, and labeling for retailers or promotional use.
თუჯის ჭურჭლის შეთავაზებების შესახებ იკითხეთ ახლავე
გთხოვთ, შეავსოთ ქვემოთ მოცემული ფორმა და ჩვენი გუნდი დაგიკავშირდებათ ფასებით, პროდუქტის დეტალებით და პერსონალიზაციის ვარიანტებით.